Factual and agile methodology (Practical Agile)
Daleelteq has adapted the XP and Scrum agile methodologies best practices to achieve projects by minimizing risks, delivering in time and fully comply with client’s requirements and needs.
Daleelteq engineers work closely with the client, the most of time they are in the client site to assure a factual comprehension of the needs by seeing how the work is done. This will allow the best design specification and a continuous optimization of the activities and business processes under the users validation to minimize the change impact and risks.
Application development begins early in the project life, we aim to deliver comprehensives and short releases to act early with the issues and users preferences and requirements.
Communication is one of the most important projects success keys, at Daleelteq we are aware that communication is not only about speaking to and hearing from people, it’s about understanding the complete message and producing the suitable products and services as they were wished and required by the customer and all the project’s stakeholders.
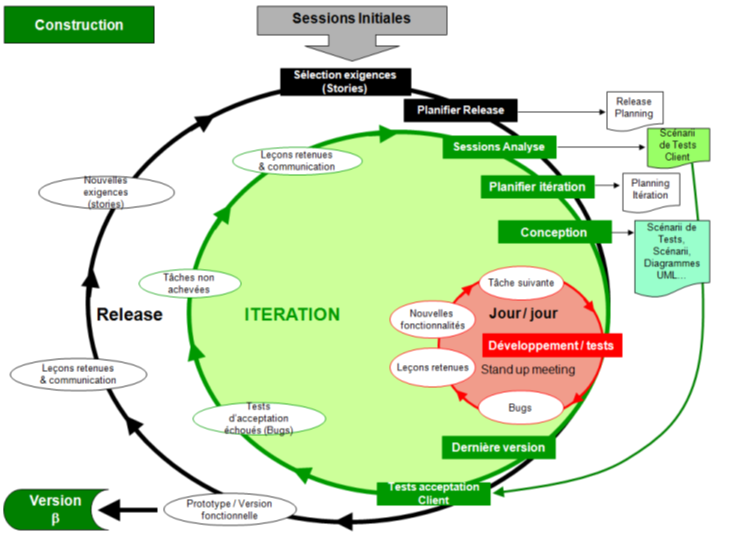
Projects Management Process Domains
To deliver the best products and services, Daleelteq have chosen to implement progressively the Capability and Maturity Model process domains to fit standards and execute projects in time, within the budget and with the required quality.
Requirements Management (REQM)
The purpose of Requirements Management (REQM) is to manage the requirements of the project’s products and product components and to identify inconsistencies between those requirements and the project’s plans and work products. This will help understanding the customer needs to produce comprehensive design and high quality products. The specific REQM goals are the folowing:
- Obtain an understanding of requirements.
- Obtain stakeholders commitment to the requirements.
- Manage changes to the requirements.
- Maintain bidirectional traceability of requirements.
- Identify inconsistencies between the project deliverables and requirements.
Daleelteq Teams share the requirements list with all the project’s stakeholders to enable rigorous monitoring and prove compliance with requirements throughout the project implementation.
Project Planning (PP)
The purpose of Project Planning (PP) is to establish and maintain plans that define project activities.
The Project Planning process area involves the following:
- Developing the project plan
- Interacting with stakeholders appropriately
- Getting commitment to the plan
- Maintaining the plan
Planning begins with requirements that define the product and project.
Planning includes estimating the attributes of the work products and
tasks, determining the resources needed, negotiating commitments,
producing a schedule, and identifying and analyzing project risks.
Iterating through these activities may be necessary to establish the
project plan. The project plan provides the basis for performing and
controlling the project’s activities that address the commitments with
the project’s customer.
The project plan will usually need to be revised as the project
progresses to address changes in requirements and commitments,
inaccurate estimates, corrective actions, and process changes. Specific
practices describing both planning and replanning are contained in this
process area.
Configuration Management (CM)
The purpose of Configuration Management (CM) is to establish and
maintain the integrity of work products using configuration
identification, configuration control, configuration status accounting,
and configuration audits.
The Configuration Management process area involves the following:
- Identifying the configuration of selected work products that compose the baselines at given points in time
- Controlling changes to configuration items
- Building or providing specifications to build work products from the configuration management system
- Maintaining the integrity of baselines
- Providing accurate status and current configuration data to developers, end users, and customers
The work products placed under configuration management include the products that are delivered to the customer, designated internal work products, acquired products, tools, and other items that are used in creating and describing these work products.
